Want to understand Renewable Energy? Curious to know Solar History? Want to learn more about how solar components and how it works? Read through our below information and get SOLARIZED yourself today!!
Renewable Solar Energy
Renewable energy is energy produced from natural sources that do not deplete or can be replenished. This energy is also known as ‘green energy’ and ‘clean energy’. There are different types of renewable energy like wind energy, solar energy, biomass energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy and wave energy.
Solar energy is the most abundant, renewable energy source in the world. Solar energy systems refer to technologies that convert the sun's heat or light to another form of energy for use. There are two categories of technologies that harness solar energy Solar Photovoltaics and Solar Thermal.
Solar Photovoltaic is a technology that converts sunlight into DC (Direct Current) electricity. Solar Thermal is a technology that utilizes the heat energy from the sun for heatingand/or the production of electricity.

Solar Energy History

Solar energy is actually nothing new. People have used solar power as far back in history as the 7th century B.C. The earliest uses of solar power included focusing the sun’s energy through a magnifying glass to start fires for cooking. Sunrooms were invented in ancient times to capture solar energy for its natural warmth.
In 1839, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect.Later in 1873, Willoughby Smith discovered that selenium could function as a photoconductor. In 1876 William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day discovered that selenium could generate electricity when exposed to light. In 1883, American inventor Charles Fritz created the first working selenium solar cell, a major precursor to the Silicon solar cell technology we used today.
In 1905,Albert Einstein published a paper on the photoelectric effect and how light carries energy generating more attention and acceptance for solar power. In 1954, three scientists from Bell Labs, Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson, created a more practical solar cell using silicon.
As the space age developed, solar panels were used to power various parts of spacecraft throughout the late 1950s and 1960s. The first was the Vanguard I satellite in 1958, followed by Vanguard II, Explorer III, and Sputnik-3.In 1964, NASA launched the Nimbus satellite, which ran entirely on its 470-watt photovoltaic solar panel array.
How Solar Works
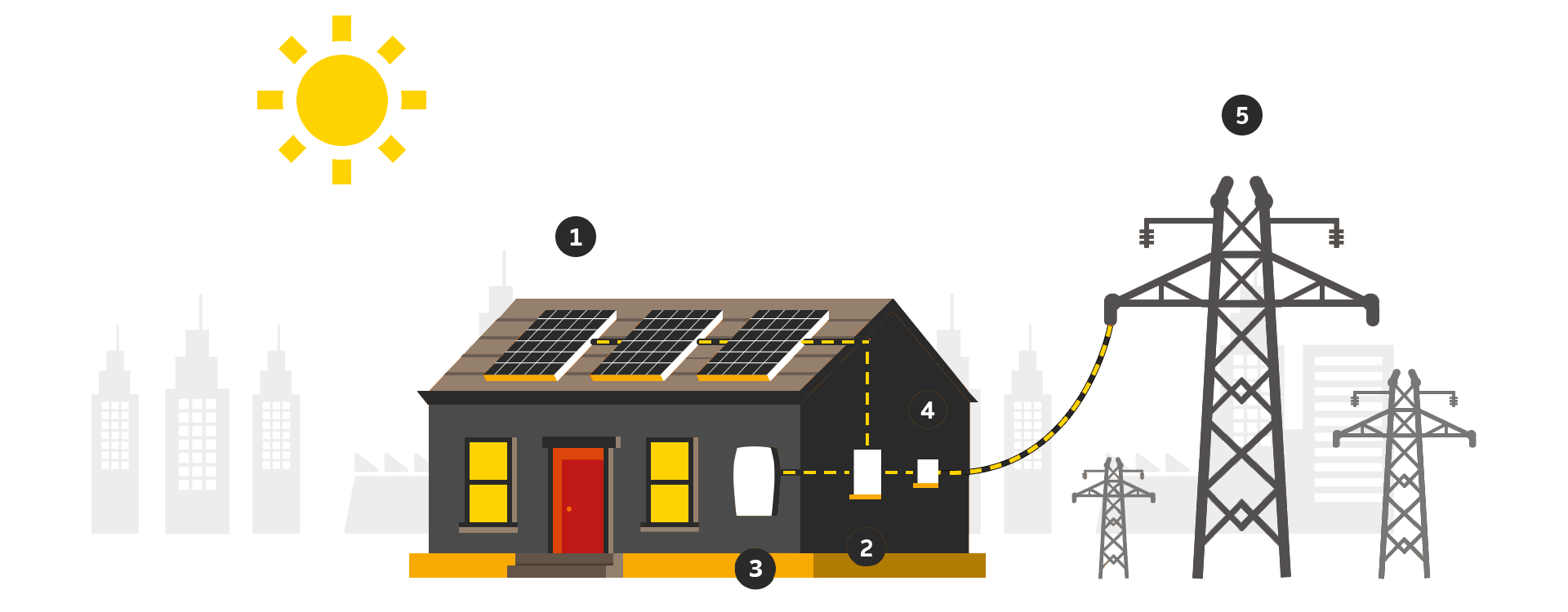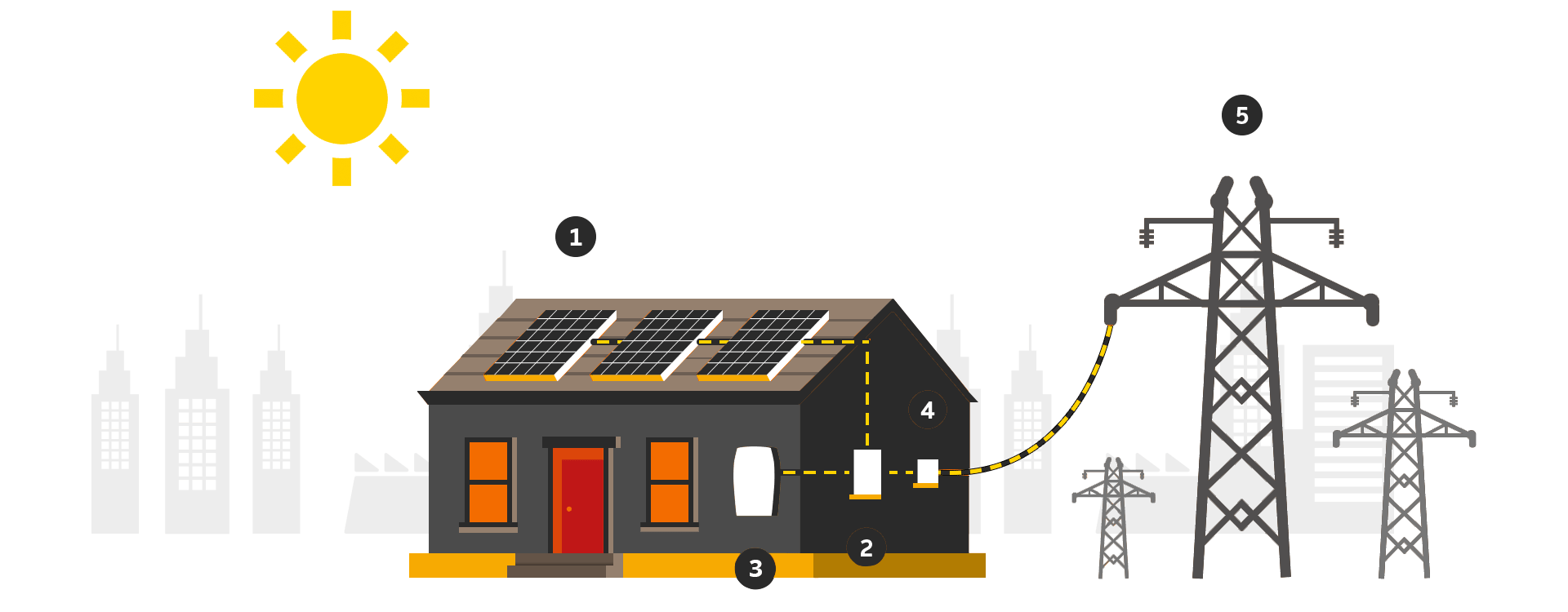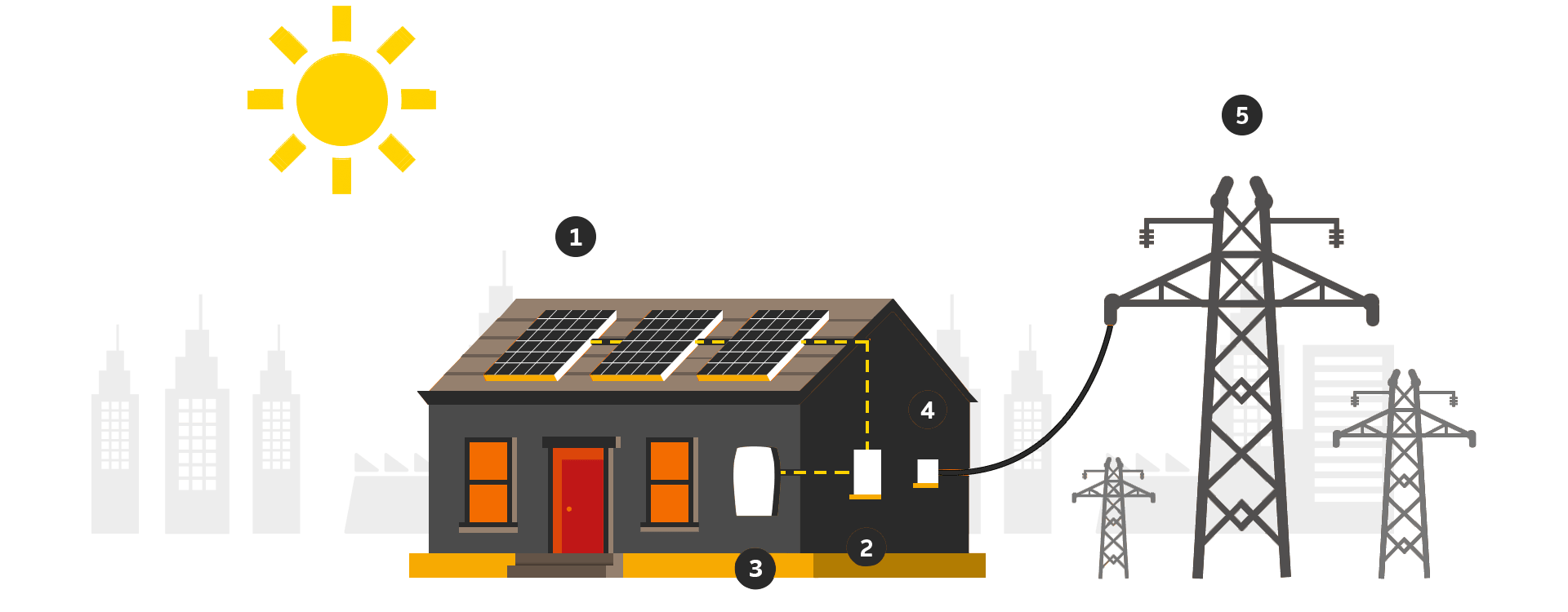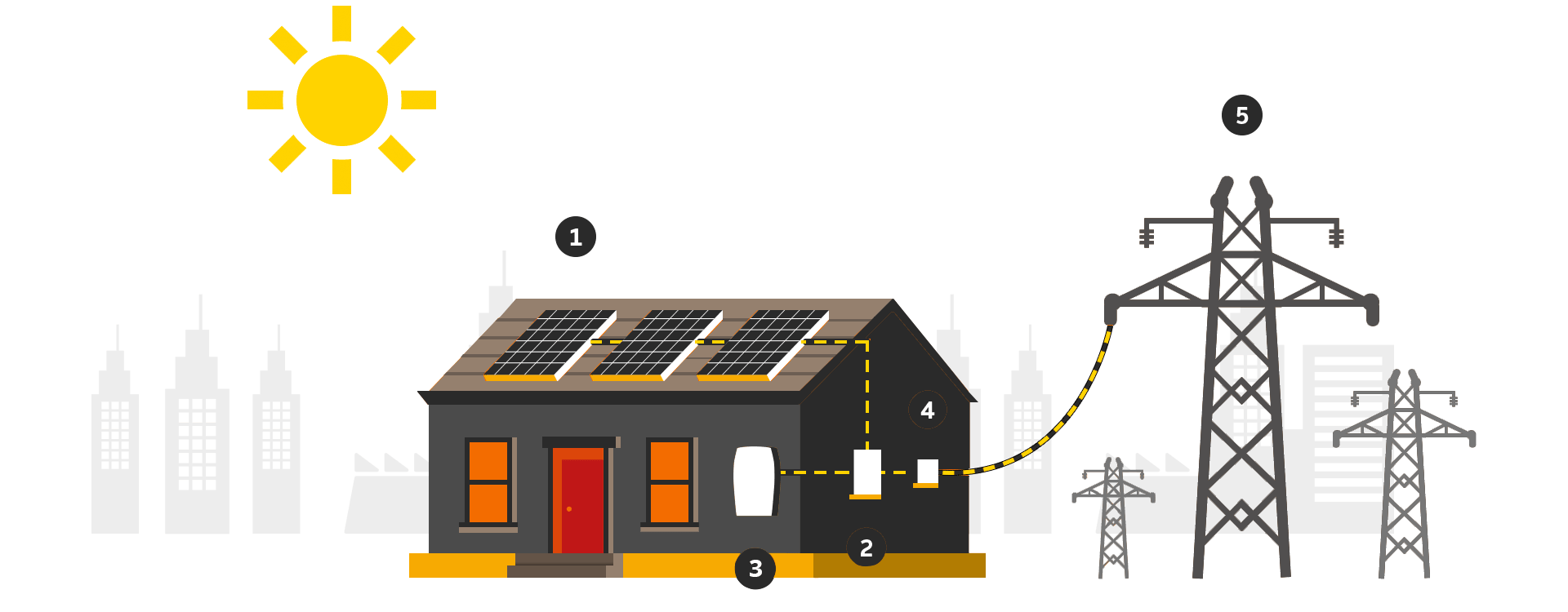
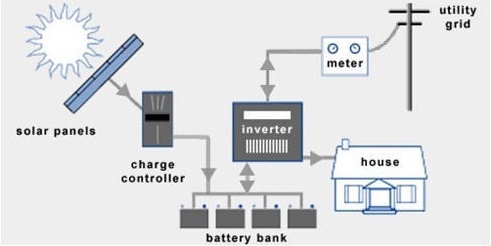
 Solar-powered Photovoltaic PV Panels convert the sun's rays into electricity by exciting electrons in silicon cells using the photons of light from the sun. Electrons are negatively charged and gets attracted to one side of the silicon cell. This creates an electric DC current.
Solar-powered Photovoltaic PV Panels convert the sun's rays into electricity by exciting electrons in silicon cells using the photons of light from the sun. Electrons are negatively charged and gets attracted to one side of the silicon cell. This creates an electric DC current.
 The DC current generated by Photovoltaic cell is converted to AC current using special electric equipment which is called Inverter.
The DC current generated by Photovoltaic cell is converted to AC current using special electric equipment which is called Inverter.
 The AC current generated by Inverter is then used by property/households and an excess current is fed to Gird.
The AC current generated by Inverter is then used by property/households and an excess current is fed to Gird.
 There is smart bi-directional meter called Net Meter which keeps the track of incoming and outgoing electrical power. This Net Metering allows users to get concessions on electricity bills as the amount for units fed to the grid will be deducted from the number of units actually consumed by the owner and the billing will only be done for that part of the units.
There is smart bi-directional meter called Net Meter which keeps the track of incoming and outgoing electrical power. This Net Metering allows users to get concessions on electricity bills as the amount for units fed to the grid will be deducted from the number of units actually consumed by the owner and the billing will only be done for that part of the units.
 Grid is termed as utility power from DESCOM. All generated energy that consumed via a provider is supplied through the grid. As shown in picture, the Grid plays an important role in designing solar system and your savings.
Grid is termed as utility power from DESCOM. All generated energy that consumed via a provider is supplied through the grid. As shown in picture, the Grid plays an important role in designing solar system and your savings.
Solar Components
Solar Panels
The solar panels also known as PV Panel/Module generate DC (direct current) electricity from sunlight. Solar panels are made up with a bunch solar cells that convert sunlight into electricity. Solar cells are made from an element called “silicon. Solar panels are installed on shadow free area of the rooftop or ground usually facing south for maximum output.
Solar panels are invented in many types and capacities. These panel varies from each other based on their formation; material used. There are 2 types of Solar Panel: -
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are often the most expensive due to the manufacturing process, which uses large amounts of highly purified silicon and a great deal of energy. Monocrystalline solar cells are about 19-20% efficient at converting sunlight to electricity. - Polycrystalline Solar Panels
To manufacture polycrystalline solar panels, low purity silicon is used.Polycrystalline cell efficiencies range between 14-16% so polycrystalline are slightly less expensive than monocrystalline ones on a price-per-Watt basis.
Inverter
A Solar Inverter is electrical equipment which converts the DC (direct current) electricity produced by the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity which is then used by the appliances or machines. Inverters play an important role in the solar energy system and are the brains of the project.Solar Inverter is the most important component of the solar system as it ensures that the maximum output of the solar panels is generated in all conditions.
There are 5 Types Of Solar Inverters:
String Inverters
These are the most common type of inverter used for residential purposes. They comes under the family of on-grid inverter.
Central Inverters
Central Inverters look like big metal cabinets. They are not suitable for homes and generally used for utility-scale solar farms or large commercial installations from few KW to MW.
Microinverters
Micro inverters are basically tiny solar inverters where they optimize each solar panel individually. It delivers more energy especially if you have partial shade conditions.
Battery Inverters
If you want to retrofit batteries to your solar power system then battery inverter is the best choice. It simply converts your battery power into the 230V AC and feeds into your switchboard where you require grid power.
Hybrid inverters
Hybrid inverters (also known as Bidirectional or magical inverters) can automatically manage between 2 or more different sources of power (grid, diesel, solar). They have features like automatic turning on/off of the diesel generator, automatic data logging, and various kinds of protection for the different components of the system.
Solar Panel Mounting Structures
Solar panels are mounted on iron fixtures so that they can withstand wind and weight of panels. The proper design of mounting structures is important to power plant performance as the power output from the PV plant will not be maximised if the mountings buckle and the panels are not optimally oriented towards the sun. In addition, improperly mounted panels present a ragged appearance that is not pleasing to the eye. Allowing sufficient air circulation to cool the PV panels is also an important factor that mounting structures should be designed
Solar Trackers
Tracking is a way of mounting the panels through a mechanism that allows the panels to follow the sun as it moves across the sky. Single-axis trackers follow the sun as it moves from East to West during the day, while dual-axis trackers also follow the sun on its North-South journey over the course of a year. Trackers can increase the power output from the PV plant but add significantly to both the initial cost of the plant and maintenance expenditure; utilization of trackers should be decided on a case-to-case basis after performing a cost-benefit analysis over the lifetime of the rooftop plant.
Bi-Directional Meter/Net Meter
The Bi-Directional Meter also called as “Net Meter” records how much electricity you send to and receive from the grid. As per the solar net metering policy in most of the states in INDIA, you will have to only pay for the difference in the electricity exported and imported every month.
Distribution Boxes
Distribution boxes in Solar PV system plays critical role in protecting electrical equipment’s from failures or any damages. There are 2 type of distribution box in Solar System.
-
Solar ACDB
It gives extra protection to the system in case of failures on load side. ACDB includes necessary surge protection device (SPD) to protect the solar inverter from any type of damage or heavy -
Solar DCDB
is used to protect the system if there is any fault during failure on DC side.DCDB controls the DC power from Solar Panels and with having necessary surge protection device (SPD) and fuses to protect the solar panels strings and solar inverter from any type of damage.
Grid
Grid is termed as utility power from DESCOM. All generated energy that consumed via a provider is supplied through the grid, we have the national grid and the state grids. The rooftop on grid solar system synchronizes with the grid electricity to ensure optimal supply of current to all your appliance or machines.
Types of Solar System
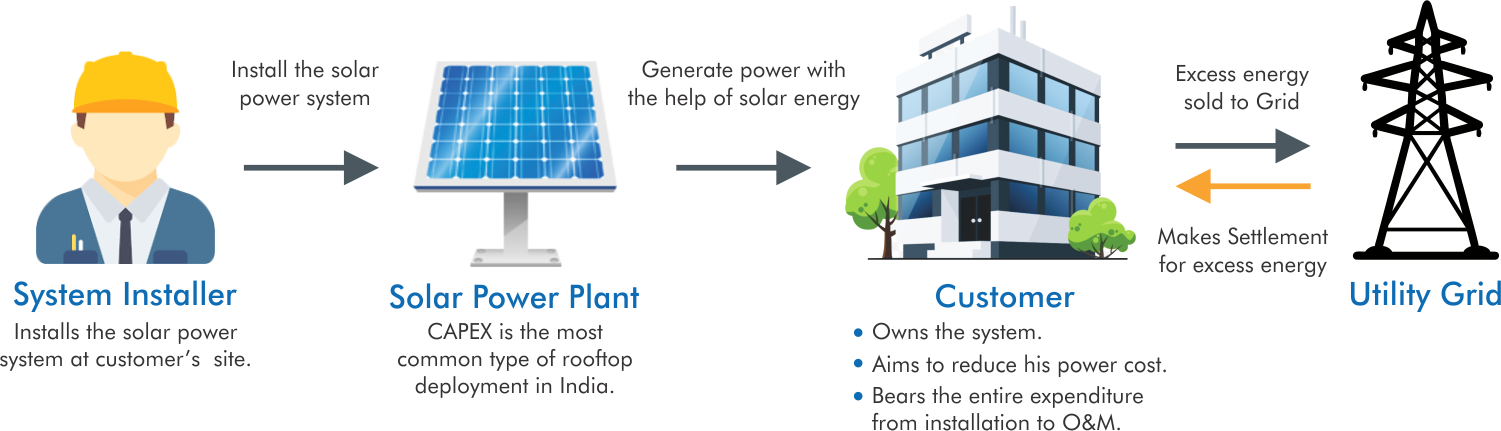
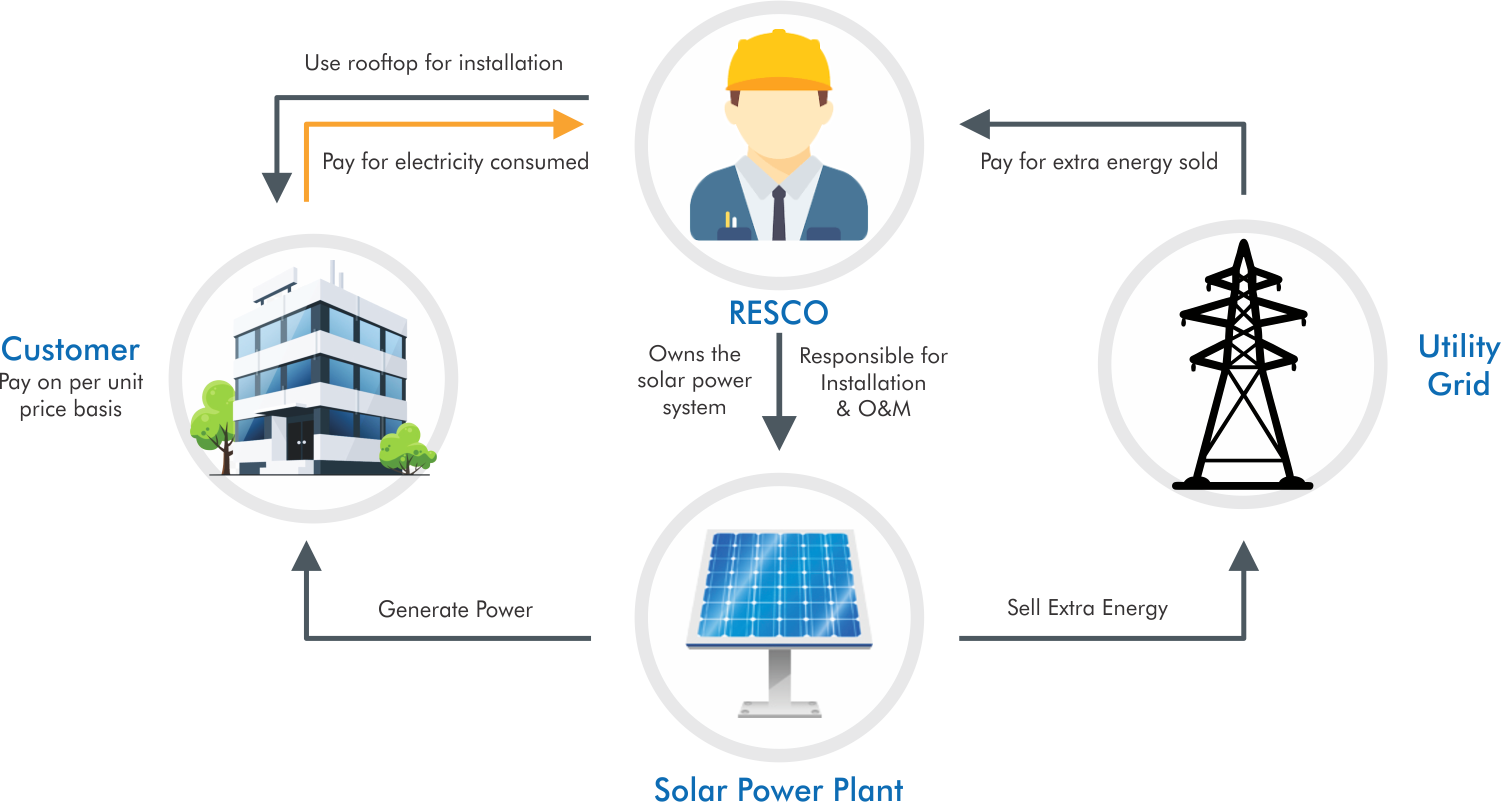
Solar Finance Model
Factors impacting solar power generation
The output power generated by a photovoltaic module and its life span depends on many aspects. Some of these factors include: the type of PV material, solar Irradiation, temperature, shading effects, inverter efficiency, dust, module orientation, weather conditions, geographical location, cable thickness etc.
Where Solar can be installed
Residential Solar
- Independent House
- Farmhouse
- Residential Societies
Industrial Solar
- Small Scale Industries
- Medium Scale Industries
- Large Scale Industries
Commercial Solar
- Shopping Malls/Complexes
- Business Centers
- Petrol Pumps
- Toll Plaza
- Hoardings
- Corporate Offices
- Independent Shops
- Sports Complexes/Stadiums
- Hospitals
- Hotels - Banquet Halls
- Restaurants and Resorts
Institutional
- Schools, Colleges, Universities
- Municipal Corporations
- Police Stations
- Railway Stations
- Bus Stands
- Metro Stations
- Airports
- Government Buildings
- Agriculture Institutes
- Gas Plants (PNG/LPG)
- Armed Force Institutes/Offices